The past seven years have been the hottest on record, according to new data from the EU’s satellite system.
The Copernicus Climate Change Service said 2021 was the fifth-warmest year, with record-breaking heat in some regions.
And the amount of warming gases in our atmosphere continued to increase.
Governments are committed to limiting global temperature rise to 1.5C to curb climate change. But scientists warn that time is fast running out.
The environmental, human and economic costs of hotter temperatures are already being seen globally.
Europe lived through its warmest summer, and temperature records in western US and Canada were broken by several degrees. Extreme wildfires in July and August burnt almost entire towns to the ground and killed hundreds.
“These events are a stark reminder of the need to change our ways, take decisive and effective steps toward a sustainable society and work towards reducing net carbon emissions,” Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, explains.
The Copernicus data comes from a constellation of Sentinel satellites that monitor the Earth from orbit, as well as measurements taken at ground level.
Fifth-warmest year
Copernicus data showed that 2021 was the fifth-hottest on record, marginally warmer than 2015 and 2018. Taken together, the past seven years were the hottest seven years on record by a clear margin, the agency explained.
The 2021 average temperature was 1.1-1.2C above the pre-industrial level around 150 years ago.
It would be easy to dismiss the latest global temperature figure as a non-event. Who celebrates fifth place in anything?
If we were in a film, these annual temperature updates would be the ominous drum beat signalling the plot is darkening.
They measure out the pace of change in our world. The increments may be tiny – a fraction of a degree – but the direction of travel is inescapable.
And make no mistake, the rhythm they mark out increasingly sets the pace for all our lives. Think of the fires and floods that affected so many people in 2021.
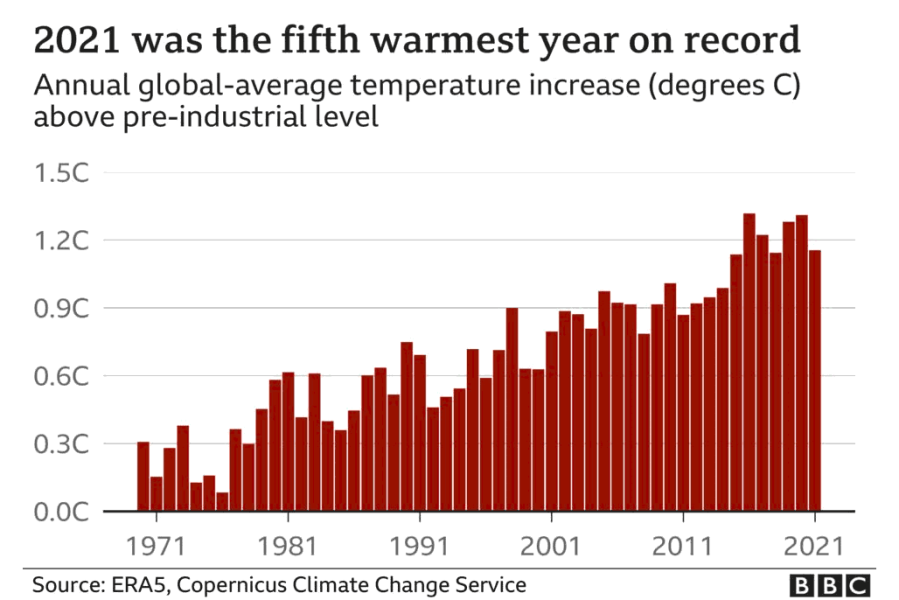
And now look again at what the data is telling us: the seven hottest years ever recorded have been the last seven years.
We can’t say we weren’t warned.
The agency said that the start of the year saw relatively low temperatures compared to recent years, but that by June monthly temperatures were at least among the warmest four recorded.
Places with above average temperatures included the west coast of US and Canada, north-east Canada and Greenland, large parts of north and central Africa, and the Middle East.
The weather phenomenon known as La Niña – when surface sea temperatures are cooler – contributed to below-average temperatures in western and eastern Siberia, Alaska, and the central and eastern Pacific during the start and end of 2021.
Europe’s warmest summer
Overall Europe’s annual temperature was outside the ten warmest years on record but the summer was the hottest.
A heatwave swept through Mediterranean in July and August, particularly affecting Greece, Spain and Italy.
In Sicily, 48.8C degrees was reported, breaking Europe’s record for highest temperature by 0.8C.
The hot temperatures in the eastern and central Mediterranean was followed by intense wildfires particular in Turkey but also in Greece, Italy, Tunisia and Algeria.
And Europe also saw extreme wet weather, with huge floods devastating parts of Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands.
These events were part of the same picture of weather systems disrupted by climate change.
Warming gases increased
The concentration in the earth’s atmosphere of two gases that significantly contribute to climate change rose in 2021, said Copernicus.
Carbon dioxide concentrations reached 414.3 parts per million last year, growing at a similar rate to 2020.
But scientists remarked that methane levels in the atmosphere increased to reach an unprecedented approximately 1,876 parts per billion. The growth rate of methane was also higher than in 2020 – Copernicus said both rates were very high compared to the past two decades of satellite data.
Scientist say it is important to reduce methane levels because it is more potent than CO2, however it lasts much less time in the Earth’s atmosphere.
The increasing concentrations of these gases showed no signs of slowing down, concluded Vincent-Henri Peuch, Director of the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service.
More data about 2021’s temperatures will be released in the coming days from other agencies including from Nasa and the UK’s Met Office.
Source: bbc.com, Photo: Mike Newbry/Unsplash